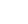
Super-Typhoon Pongsona, December 2002
Packing gusts of nearly 300 kilometers per hour (184 miles per hour) and sustained winds of 240 kilometers per hour (150 miles per hour), Super-Typhoon Pongsona struck the U.S. Island of Guam on December 8, 2002. This 3D model of the hurricane shows the outline of the clouds, based on cloud top heights derived from observations from the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument on NASA's Aqua Satellite.
The color overlay represents the brightness temperatures observed in one of the Humidity Sounder for Brazil (HSB) channels. HSB also flies aboard NASA's Aqua Satellite.
Blue areas indicate intense convection and rain, while green and yellow reflect the internal temperature of the clouds. Microwaves, unlike infrared radiation, penetrate clouds and look into them or even through them. Red, most of which has been removed from the picture for clarity, represents areas where HSB penetrates all the way to the surface.