Comparing Radiosondes to CLIMCAPS profiles
Convolving radiosondes and ozonesondes to satellite sounding retrievals
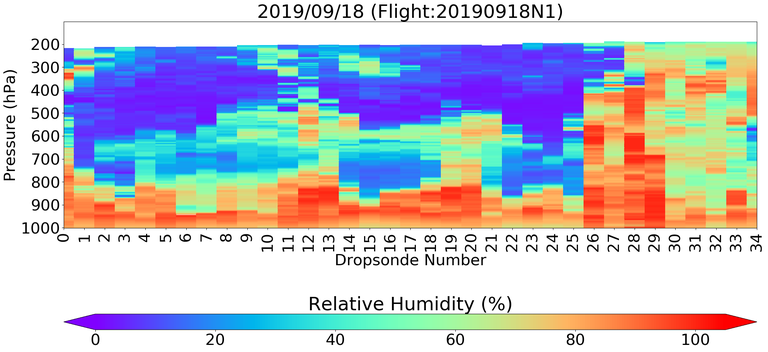
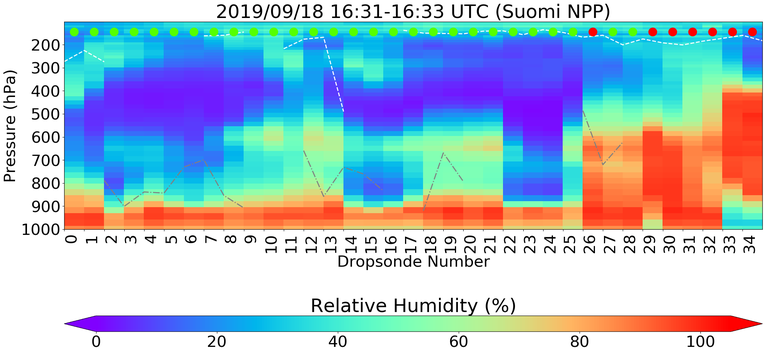
A common practice is to convolve radiosondes and ozonesondes to satellite sounding retrievals to ease interpretation in some applications. Sondes have much higher vertical resolution, vertical sampling and vertical structure, compared to satellite soundings like those found in CLIMCAPS (Figure 1).
Inter-comparisons can become difficult without convolving the higher-resolution measurement to the lower-resolution one because differences may arise due to variation in quality or they may simply reflect differences in measurement characteristics, such as footprint size and vertical resolution.
We illustrate how to convolve one set of measurements (e.g., ozonesondes) with O3 profiles from CLIMCAPS in Section 3.
Figure 1: A research flight on September 18, 2019 shows the relative humidity profiles (a) from dropsondes released from a Gulfstream-IV “Hurricane Hunter” aircraft and (b) derived from CLIMCAPS-SNPP H2O retrieval. The colored dots indicate if the MW+IR retrieval passed (green) or failed (red) using footprint quality control. No averaging kernel convolution has been applied to the radiosonde data. More information on this case study is in Section 2.3.1 of the Water Vapor chapter.
NUCAPS validation studies
If your application requires comparing CLIMCAPS to radiosondes, we recommend reviewing past work inter-comparing NOAA-Unique Combined Atmospheric Processing System (NUCAPS) with radiosondes. NUCAPS is the model-independent sister algorithm to CLIMCAPS that was developed for real-time hazardous weather monitoring. Since both algorithms have the same vertical resolution, methods used to compare NUCAPS with "truth" observations such as radiosondes are appropriate to use for CLIMCAPS. The following NUCAPS validation studies may thus be helpful for evaluating CLIMCAPS:
- Divakarla, M. G., Barnet, C. D., Goldberg, M. D., McMillin, L. M., Maddy, E., Wolf, W., et al.: Validation of Atmospheric Infrared Sounder temperature and water vapor retrievals with matched radiosonde measurements and forecasts. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 111(D9). https://doi.org/10.1029/2005JD006116, 2006.
-
Feltz, M. L., Knuteson, R. O., Revercomb, H. E., & Tobin, D. C. A methodology for the validation of temperature profiles from hyperspectral infrared sounders using GPS radio occultation: Experience with AIRS and COSMIC. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 119(3), 1680–1691. https://doi.org/10.1002/2013JD020853, 2014.
- Feltz, M. L., Borg, L., Knuteson, R. O., Tobin, D., Revercomb, H., & Gambacorta, A.: Assessment of NOAA NUCAPS upper air temperature profiles using COSMIC GPS radio occultation and ARM radiosondes. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 122(17), 9130–9153. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017JD026504, 2017.
- Nalli, N. R., Gambacorta, A., Liu, Q., Barnet, C. D., Tan, C., Iturbide-Sanchez, F., Reale, T., Sun, B., Wilson, M., Borg, L. and Morris, V. R.: Validation of Atmospheric Profile Retrievals From the SNPP NOAA-Unique Combined Atmospheric Processing System. Part 1: Temperature and Moisture, IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 56(1), 180–190, doi:10.1109/TGRS.2017.2744558, 2018a.
- Nalli, N. R., Gambacorta, A., Liu, Q., Tan, C., Iturbide-Sanchez, F., Barnet, C. D., Joseph, E., Morris, V. R., Oyola, M. and Smith, J. W.: Validation of Atmospheric Profile Retrievals from the SNPP NOAA-Unique Combined Atmospheric Processing System. Part 2: Ozone, IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 56(1), 598–607, doi:10.1109/TGRS.2017.2762600, 2018b.
- Sun, B., Reale, A., Tilley, F. H., Pettey, M. E., Nalli, N. R., & Barnet, C. D. Assessment of NUCAPS S-NPP CrIS/ATMS Sounding Products Using Reference and Conventional Radiosonde Observations. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 10(6), 2499–2509. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTARS.2017.2670504, 2017.