Mission & Instrument
The AIRS instrument has provided the most significant increase in forecast improvement in this time range of any other single instrument
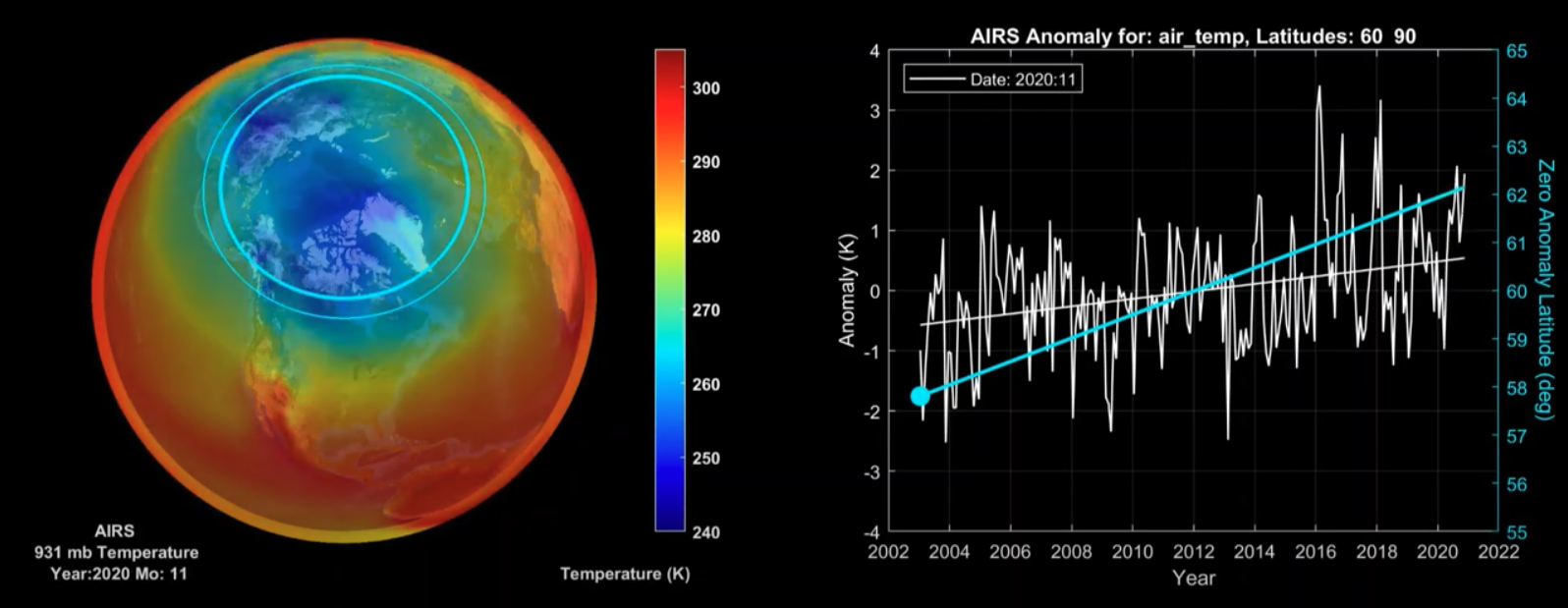
Launched into orbit on May 4, 2002 aboard NASA's Aqua satellite, the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder, or AIRS, is enhancing our understanding of Earth's weather and climate. AIRS is one of six instruments aboard NASA's Aqua satellite, which in turn is part of a constellation of satellites that make up NASA's Earth Observing System. AIRS along with its partner microwave instrument the Advanced Microwave Sounding Unit (AMSU-A), represents the most advanced atmospheric sounding system ever deployed in space. Together these instruments observe the global water and energy cycles, climate variation and trends, and the response of the climate system to increased greenhouse gases.
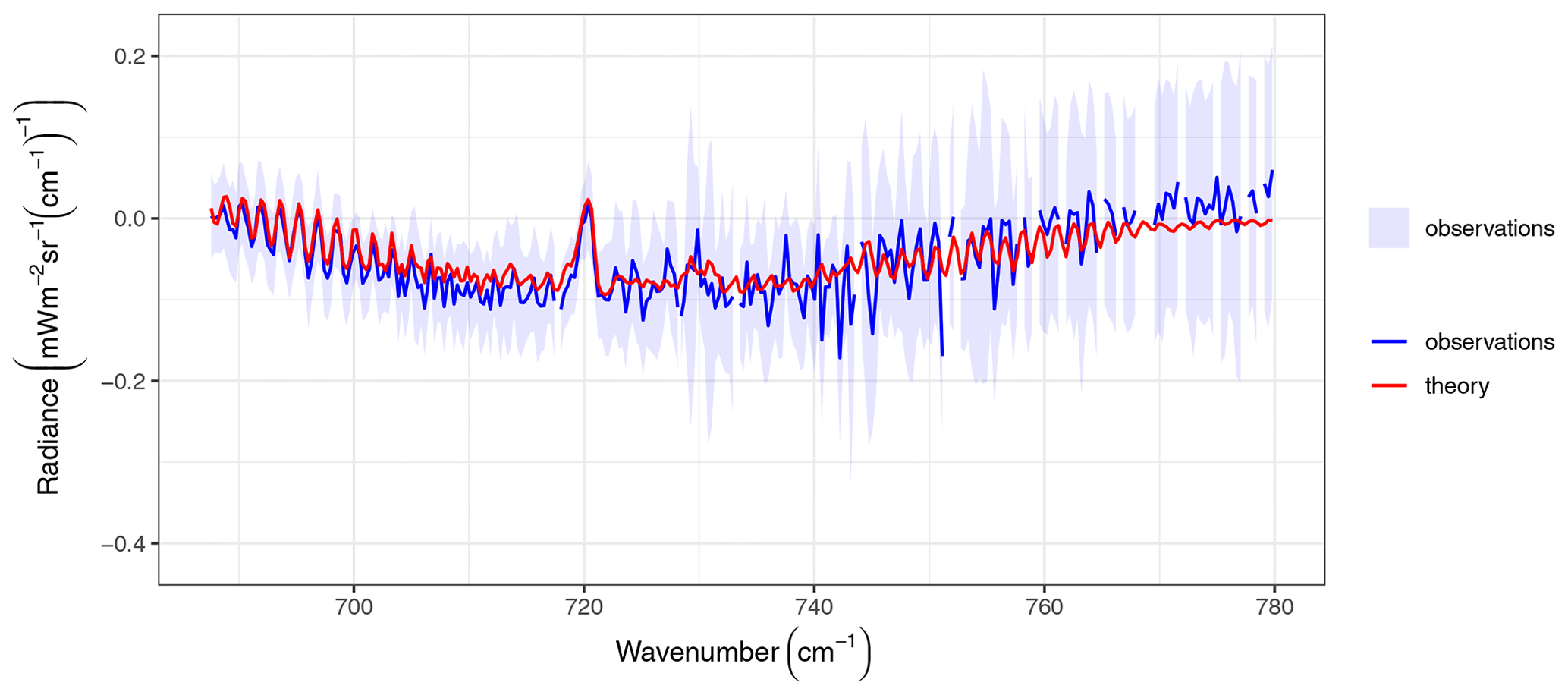
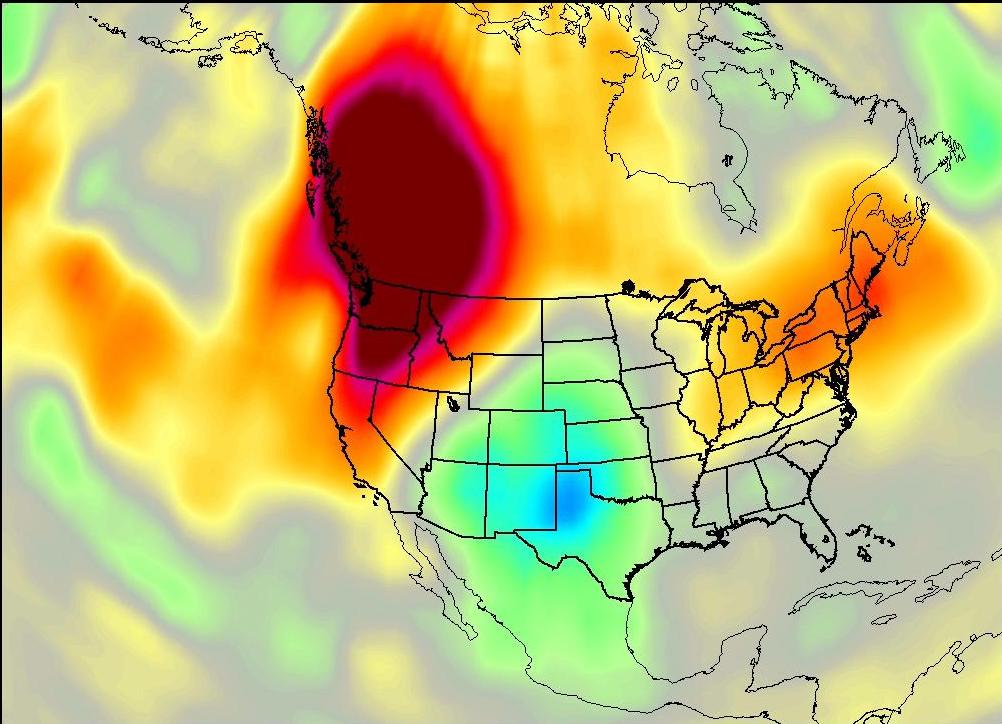
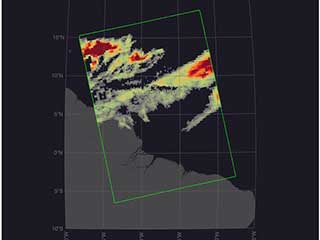
AIRS uses cutting edge infrared technology to create three-dimensional maps of air and surface temperature, water vapor, and cloud properties. With 2378 spectral channels, AIRS has a spectral resolution more than 100 times greater than previous infrared sounders and provides more accurate information on the vertical profiles of atmospheric temperature and moisture. AIRS can also measure trace greenhouse gases such as ozone, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, and methane.