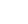
Arctic Carbon Dioxide, February 2010 to February 2011
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder, AIRS, was launched aboard the Aqua Spacecraft in 2002 as part of NASA's Earth Observing System Afternoon Constellation of satellites known as the 'A-Train. The most important trace gas retrieved by AIRS for the study of anthropogenic effects on climate is carbon dioxide. AIRS CO2 retrievals use an analytical method for the determination of carbon dioxide and other minor gases in the troposphere from AIRS spectra. AIRS has provided the first satellite retrieval of mid-tropospheric CO2 under cloudy conditions, without the use of a priori information from models. AIRS retrievals use cloud-cleared thermal IR radiance spectra in the 15 micron band with an accuracy better than 2 ppm, making it ideal for mapping the distribution and transport of carbon dioxide levels in the free troposphere.
Arctic CO2 in the mid-troposphere (8-12 km altitude) over the period February 2010 through February 2011. The AIRS data have been combined over a 9-day window and then assimilated by a Fixed Rank Kriging (FRK) process that smoothes the data based upon spatial covariances that are neither stationary nor isotropic. The FRK methodology was developed by a group in the Program in Spatial Statistics and Environmental Sciences at The Ohio State University.