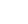
Carbon Monoxide from Fires in Greece, 2007
A series of fires across Greece in August of 2007 burned 469,000 acres and claimed the lives of 65 people. The fires, in which an estimated 4,000 people lost their homes, mostly occurred in the southern part of of the country.
In this visualization, the carbon monoxide signature from the fires in Greece is revealed in data retrieved by the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) on NASA's Aqua spacecraft. Forest fires create large amounts of carbon monoxide. AIRS provides daily global maps of carbon monoxide from space, allowing scientists to follow the global transport of this gas day-to-day. This visualization shows the amount of Carbon monoxide that has risen 2 to 8 kilometers (6,500 ft to 26,200 ft altitude) from August 24-28, 2007. More carbon monoxide generally means more pollution, either natural from wildfires or from industrial and domestic sources.
Beginning August 24, a significant plume emanates from the extensive fires burning in Greece. This plume moves southeast across the Mediterranean Sea and over North Africa from August 24 to 28. It crosses to Africa and arcs westward over the Sahara Desert and continues to curl around over the Eastern Mediterranean toward Sardinia and Corsica.
More information about AIRS can be found at airs.jpl.nasa.gov.